Succinic acid, 99+%
CAS: 110-15-6
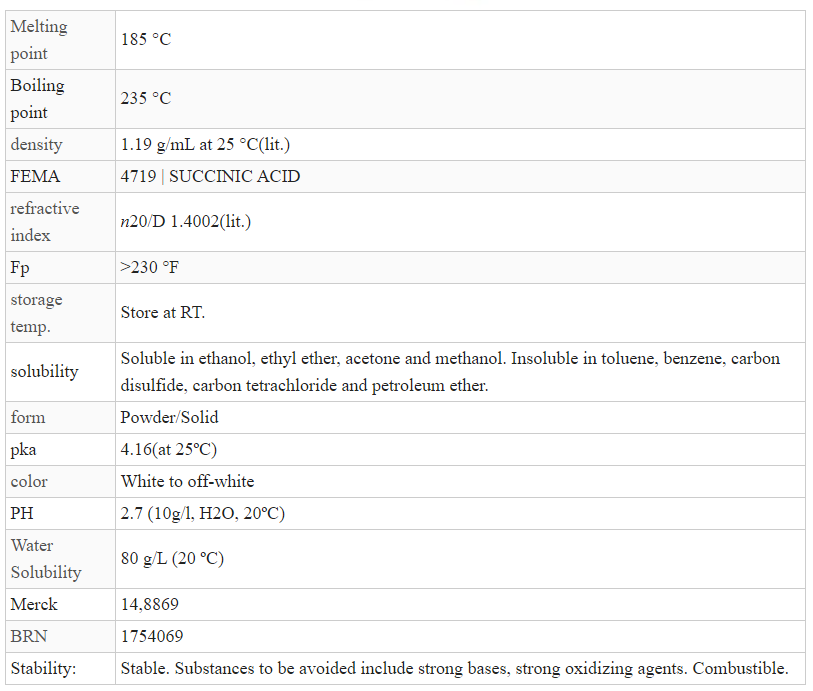
[110-15-6], HO2CCH2CH2CO2H, F.W. 118.09, m.p. 186-188°, b.p. 235°, f.p.
206°(402°F), d. 1.56, EINECS 203-740-4, RTECS WM4900000, BRN 1754069, MDL
MFCD00002789, TSCA Yes
Hazard Codes: H303-H318
Precautionary code (EU): P261-P270-P271-P280-P304+P340-P305+P351+P338-P310-P403+P233-P501c
Hwang, H. J.; Choi, S. P.; Lee, S. Y.; Choi, J. I.; Han, S. J.; Lee, P. C.
Dynamics of membrane fatty acid composition of succinic acid-producing
Anaerobiospirillum succiniciproducens. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 193, 130-133.
Gunnarsson, I. B.; Kuglarz, M.; Karakashev, D.; Angelidaki, I.
Thermochemical pretreatments for enhancing succinic acid production from
industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 182, 58-66.
Description
Succinic acid is a dicarboxylic acid. The anion, succinate, is a component
of the citric acid cycle capable of donating electrons to the electron transfer
chain. Succinic acid is created as a byproduct of the fermentation of sugar. It
lends to fermented beverages such as wine and beer a common taste that is a
combination of saltiness, bitterness and acidity. Succinate is commonly used as
a chemical intermediate, in medicine, the manufacture of lacquers, and to make
perfume esters. It is also used in foods as a sequestrant, buffer, and a
neutralizing agent. Succinate plays a role in the citric acid cycle, an
energy-yielding process and is metabolized by succinate dehydrogenase to
fumarate. Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) plays an important role in the
mitochondria, being both part of the respiratory chain and the Krebs cycle. SDH
with a covalently attached FAD prosthetic group, binds enzyme substrates
(succinate and fumarate) and physiological regulators (oxaloacetate and ATP).
Oxidizing succinate links SDH to the fast-cycling Krebs cycle portion where it
participates in the breakdown of acetyl-CoA throughout the whole Krebs cycle.
Succinate can readily be imported into the mitochondrial matrix by the
n-butylmalonate- (or phenylsuccinate-) sensitive dicarboxylate carrier in
exchange with inorganic phosphate or another organic acid, e.g. malate. (1)
Mutations in the four genes encoding the subunits of succinate dehydrogenase are
associated with a wide spectrum of clinical presentations (i.e.: Huntington's
disease. (2). Succinate also acts as an oncometabolite. Succinate inhibits
2-oxoglutarate-dependent histone and DNA demethylase enzymes, resulting in
epigenetic silencing that affects neuroendocrine differentiation.
Search term: 110-15-6 (Found by approved synonym)
Succinic acid
Molecular Formula:C4H6O4
Average mass:118.088 Da
Monoisotopic mass118.026611 Da
ChemSpider ID1078
Appearance:Powder or crystalline or granules
Physical State:Solid
Storage:Store at room temperature
Melting Point:185-190° C
Boiling Point:235° C
Anti-Biotin Antibody (33): sc-101339
Biotin, a water-soluble B complex vitamin, is required by all organisms but
can only be synthesized by yeasts, molds, algaes, some plant species and
bacteria. Biotin, a tetrahydrothiophene ring fused with an ureido
(tetrahydro-imidizalone) ring, is important in the catalysis of essential
metabolic reactions to synthesize fatty acids, to metabolize leucine and in
gluconeogenesis. Human intestinal bacteria generally produce in excess of the
body′s daily Biotin requirement. The occurrence of Biotin in nature is
widespread and, although extremely rare, Biotin deficiency is associated with
dermatitis, nausea, loss of hair, depression, muscle pain, and reproductive
disturbances.
SynonymsDatabase
1,2-Ethanedicarboxylic acid
1,4-Butanedioic acid
110-15-6 [RN]
203-740-4 [EINECS]
4-02-00-01908 [Beilstein]
Acide butanedioique [French]
Acide succinique [French] [ACD/IUPAC Name]
Acido succinico [Italian]
ácido succínico [Spanish]
ácido succínico [Portuguese]
acidum succinicum [Latin]
Bernsteinsaeure [German]
Bernsteins?ure [German] [ACD/IUPAC Name]
Butanedioic acid [ACD/Index Name]
HOOC-CH2-CH2-COOH [Formula]
Kyselina jantarova [Czech]
MFCD00002789 [MDL number]
QV2VQ [WLN]
Succinic acid [ACD/IUPAC Name] [Wiki]
Succinic acid
Ηλεκτρικ? οξ? [Modern Greek (1453-)]
Янтарная кислота [Russian]
コハク酸 [Japanese]
琥珀酸 [Chinese]
14493-42-6 [RN]
152556-05-3 [RN]
21668-90-6 [RN]
61128-08-3 [RN]
acidum succinicum
amber acid
asuccin
Bernsteinsaeure
Bernsteinsaure
Butandisaeure
BUTANE DIACID
BUTANEDIOICACID
CpeE protein
DB00139
Dihydrofumaric acid
Ethanedicarboxylic acid
Ethylene dicarboxylic acid
Ethylene succinic acid
FMR
fum
Fumaric acid [Wiki]
http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0000254
https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/searchId.do?chebiId=CHEBI:15741
Katasuccin
Kyselina jantarova
MAE
Maleic acid [Wiki]
Sal succini
STR02803
Succinellite
Succinic acid 100 ?μg/mL in Acetonitrile
succinic acid(free acid)
Succinic acid, ACS grade
SUCCINIC-D4 ACID
succunic acide
Wormwood acid
For Research Use Only. Not Intended for Diagnostic or Therapeutic Use.
186-188 °C Alfa Aesar
185 °C Indofine [15-0400] , [15-0400]
185 °C OU Chemical Safety Data (No longer updated) More details
184-189 °C Merck Millipore 3821, 822260
185 °C Jean-Claude Bradley Open Melting Point Dataset 16121
186.5 °C Jean-Claude Bradley Open Melting Point Dataset 16582
188 °C Jean-Claude Bradley Open Melting Point Dataset 13519, 22290,
28530
187 °C Jean-Claude Bradley Open Melting Point Dataset 8429
186-188 °C Alfa Aesar A12084, 33272
188-190 °C SynQuest
184-186 °C Oakwood
184-186 °C (Literature) LabNetwork (old) LN00193188
185 °C Indofine [15-0400] , [15-0400] , [15-0400]
184-185 °C FooDB FDB001931
188-190 °C SynQuest 2121-1-24
184-186 °C Cayman Chemical CM247712
184-186 °C Chemenu CM247712
184-186 °C Sigma-Aldrich ALDRICH-134384
185 °C Kaye & Laby (No longer updated)
184-186 °C Oakwood 104604, 239121
Toxicity Profile
Route of Exposure
Eye contact, Inhalation, Ingestion.
Mechanism of Toxicity
Succinate can inhibit the activities of α-KG–dependent oxygenases (KDMs)
and the TET family of 5-methlycytosine (5mC) hydroxylases. Succinate also
mediates allosteric inhibition of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) prolyl
hydroxylases (PHDs). Inhibition of HIF PHDs leads to activation of HIF-mediated
pseudohypoxic response, whereas inhibition of KDMs and TET family of 5mC
hydroxylases causes epigenetic alterations that ultimately cause cancer.
Succination of KEAP1 in FH deficiency results in the constitutive activation of
the antioxidant defense pathway mediated by NRF2, conferring a reductive milieu
that promotes cell proliferation. Succination of the Krebs cycle enzyme Aco2
impairs aconitase activity in Fh1-deficient MEFs. Succination also causes
irreversible inactivation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
(GAPDH).
Metabolism
Succinic acid can be converted into fumaric acid by oxidation via succinate
dehydrogenase.
Toxicity Values
Acute oral toxicity (LD50): 2260 mg/kg [Rat].
Lethal Dose
Not Available
Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification)Not listed by IARC. Has been
implicated in oncogenesis (17).
Uses/Sources
Succinic acid is a precursor to some specialized polyesters. It is also a
component of some alkyd resins. Succinic acid is used in the food and beverage
industry, primarily as an acidity regulator. It is also sold as a food additive
and dietary supplement, and is generally recognized as safe by the US FDA.
Minimum Risk Level
Not Available
Health Effects
Symptoms
Acute Exposure: the clinical signs of acute toxicity are weakness and
diarrhea.
Treatment
EYES: irrigate opened eyes for several minutes under running water.
INGESTION: do not induce vomiting. Rinse mouth with water (never give anything
by mouth to an unconscious person). Seek immediate medical advice. SKIN: should
be treated immediately by rinsing the affected parts in cold running water for
at least 15 minutes, followed by thorough washing with soap and water. If
necessary, the person should shower and change contaminated clothing and shoes,
and then must seek medical attention. INHALATION: supply fresh air. If required
provide artificial respiration.
Substituents
Fatty acid
Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
Carboxylic acid
Organic oxygen compound
Organic oxide
Hydrocarbon derivative
Organooxygen compound
Carbonyl group
Aliphatic acyclic compound
Succinic acid use and synthesis method
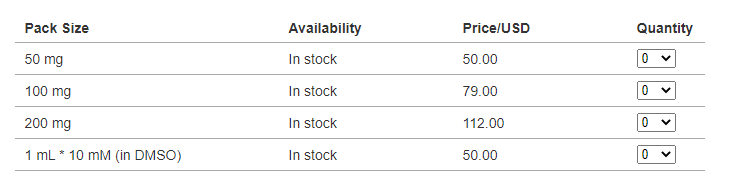
About Price